The International Tinnitus Journal
Official Journal of the Neurootological and Equilibriometric Society
Official Journal of the Brazil Federal District Otorhinolaryngologist Society
ISSN: 0946-5448

Google scholar citation report
Citations : 12717
The International Tinnitus Journal received 12717 citations as per google scholar report
The International Tinnitus Journal peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Excerpta Medica
- Scimago
- SCOPUS
- Publons
- EMBASE
- Google Scholar
- Euro Pub
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Medicus
- Medline
- PubMed
- UGC
- EBSCO
Volume 28, Issue 2 / September 2024
Research Article Pages:198-204
10.5935/0946-5448.20240029
Assessing the Quality of Nursing Care in Tinnitus Management: A Systematic Review
Authors: Samia Musaad Almutairi, Arwa Khalid Qahtani, Najla Andullah Althobaiti, Tahani Ebrahim Daghriri, Arwa Sanad Alfelit, Ebtihal Jamaan Althagafi, Njood Mohammed Hamzi, Reem Fahad Alenzy, Maram Fahad Alenzy, Ashwaq Fahad Alanazi
PDF
Abstract
Background: It is however important to note that tinnitus management in Saudi Arabia has some peculiarities mainly relating to the quality of nursing care. Surprisingly only a few studies have been conducted to ascertain the existing nursing practices and its relation to tinnitus patient outcomes. Aim: This research is set to systematically map and evaluate the quality of nursing care of tinnitus in Saudi Arabia to establish the strengths and weaknesses and offer suggestions for enhancement. Method: The systematic review was done with help of databases PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Only articles between the years 2019 and 2024 were considered for the review along with the aspects of quality of nursing care in tinnitus. Descriptive data were collected and analyzed for assessing the quality and the care compliance in different settings within Saudi Arabia. Result: The review also indicated that there is widespread variation in the quality of nursing care with several studies pointing at deficiencies in compliance with the standard of care. Some of main concerns were identified as lack of preparation and absence of guidelines. However, some of the research works pointed out some gains linked to comprehensive care models and higher awareness. Conclusion: Thus, the present research calls for the development of the specific protocols and the improvement of the educational courses for the Saudi nurses dealing with tinnitus. These gaps have potential for the enhancement of the quality of patient care and the benchmarking of practices with international standards for the better management of tinnitus thus enhancing patient outcomes in this part of the world.
Keywords: Quality of nursing care, Tinnitus management, Saudi arabia, Systematic review
Introduction
Tinnitus refers to the condition in which the patient hears a sound that does not exist, and impacts on QOL. It is considered very bothersome [1,2]. In KSA, the increasing occurrence of tinnitus among the community has created the increasing demand for its management in the health care sector [3]. Considering the cultural and healthcare importance of the disease, there is a rising necessity for adequate and improved care for patients with this disease, and this is due to rising life expectancy due to improved healthcare systems [4].
The approach taken in Saudi Arabia for a patient suffering from tinnitus is medical, psychological and supportive [5]. However, past evidences have been given a close study to the quality of care the patient gets from the nurse in this context. Nurses have an important duty of providing care that involves not only procedures but also warmth, words of encouragement and lessons that patients need to know [6]. The impact of these nursing interventions that are being implemented to enhance patients’ quality of life especially those with tinnitus is an important area of assessment [7].
It is most important to recognize that tinnitus is multidimensional in its nature and must be addressed with an equally complex solution that will include the best of clinical scientific evidence as well as the contextual factors of culture [8]. There are certain areas that would affect the quality of nursing care in Saudi Arabia; the training, the tools that is available to the nurses, and the protocols in place. This research study seeks to assess the extent to which these factors enhances the quality of care provided to tinnitus patients to have an understanding of the gaps that needs to be filled [9].
It becomes important to know the quality of the nursing care provided in Saudi Arabia for treatment of tinnitus and its management with respect to cultural aspect. As a result, the study focuses to fill the existing gaps in knowledge in the following ways: From the findings, this study would be able to make recommendations that can be implemented in policy changes, changing and improving the nursing education, and subsequently the improvement on the management of tinnitus patients in the Kingdom.
Problem Statement
This paper explores tinnitus as a particular clinical concern in Saudi Arabia and more generally the challenges that exist in managing tinnitus through the healthcare system and the deficiency of knowledge and implementation of QCNP [10]. While tinnitus is becoming more and more common, there is a deficiency of research that evaluates the quality of nursing care for tinnitus focused. Such deficiencies in the available literature undermine the approaches taken to offer timely effective tinnitus patient-centered, comprehensive care that meets the targeted patient’s complex needs.
Significance of the Study
The importance of this study rests with the fact that this research will help to fill the identified knowledge deficit and enhance the quality of nursing care for tinnitus patients within Saudi Arabia [11]. In light of the above argument, the following are the objectives of this research; This research seeks to achieve the following specific objectives to conduct a systematic and detailed research on the current practices and come up with areas that could be improved upon, as well as put in place standards that could be useful in the delivery of quality care [12]. The findings of this research are important for the future development of healthcare policies and training programs, which will allow improving the overall satisfaction of patients, and the effectiveness of treatments offered to them. Increase in the quality of care in tinnitus as a nursing care problem reflects the general objective of Saudi Arabia healthcare, which seeks to advance quality and patients’ welfare [13].
Aim of the Study
The purpose of this research therefore is to undertake a systematic review that evaluates the quality of care delivered to patients with tinnitus in KSA [14]. With the intention of enhancing the efficiency of nursing intervention in tinnitus the present research endeavors to assess the current practices and in turn, evaluate the existing care gaps for making quality recommendations. Such a study will help the development of guidelines and standards that will help to deliver patient-centered, quality, and consistent care in compliance with the objectives of the Saudi Arabia health care system [15].
Methods
Research Question (PICOT Question)
In this study proposing by the nurse researcher in Saudi Arabia, the following research question and hypothesis have been formulated: Research question: among patients with tinnitus (P), what is the impact of quality of nursing care (I) over standard care practices (C) in tinnitus management concerning the success rate of patients’ satisfaction and the degree of tinnitus relief perceived by the patient within six months (T)?
Search Strategy
To ensure the validity of the proposed concept, a specific approach will be taken to evaluate the quality of nursing care in tinnitus management to Saudi Arabia. The approach involved screening for the studies through different database electronic and restricting the search to Saudi context only literature. This approach involved an evaluation of peer-reviewed articles, clinical reference materials and resources focusing on nursing care for tinnitus patients. Much attention was paid to search for the source that would present success rates of various interventions on the background of patient outcomes within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Search Syntax
("Tinnitus management" OR "Tinnitus care" OR "Ringing in ears management")
AND
("Quality of nursing care" OR "Nursing interventions" OR "Nurse-led care")
Database Selection:
This undertaking was done in sundry of the electronic databases relevant to health care and medical research, including PubMed, Scopus, and the Saudi Digital Library. These databases were selected because they offer full coverage of health-related literature and can offer information on studies that are likely to be relevant to Saudi Arabia. In addition, the local health care journals and publications were also perused to incorporate the regional containments and principles.
Selection Criteria:
The criteria for inclusion were therefore; the studies had to concern nursing care quality in the management of tinnitus within Saudi Arabia, must have been published in English/Arabic language, and were conducted within the last 5 years (2019-2024). Studies that were non-Saudi, non-nursing interventional studies and articles that did not specifically address tinnitus management were excluded. This helped in the elimination of any obsolete work as well as the consideration of only the most recent works in determination of the quality of the nursing care in the specified context.
Literature Search:
The literature search for identifying the existing research based on quality of nursing care for tinnitus patients in Saudi Arabia included a search of different electronic databases such as PubMed, Scopus and Saudi Digital Library. The keywords used for searching the articles included tinnitus, tinnitus management, nursing care and Saudi Arabia. Hence, this approach aimed at establishing the effectiveness of nursing interventions as well as their effects on tinnitus management in Saudi Arabia.
Study Selection Flow Chart:
The procedure of inclusion and exclusion of the studies was based on the title and abstracts of the studies found regarding the management of tinnitus and nursing care in Saudi Arabia. The nurses and patient outcome in Saudi Arabia then screened all the studies in full text to make sure they met the inclusion criteria that was the quality of care provided. Finally, eight research studies were considered for comparisons and analysis after applying both, the inclusion and the exclusion criteria mentioned earlier. The flow chart can be used to represent the screening process of the studies from identification until selection and shows the number of studies rejected at each phase (Figure 1).
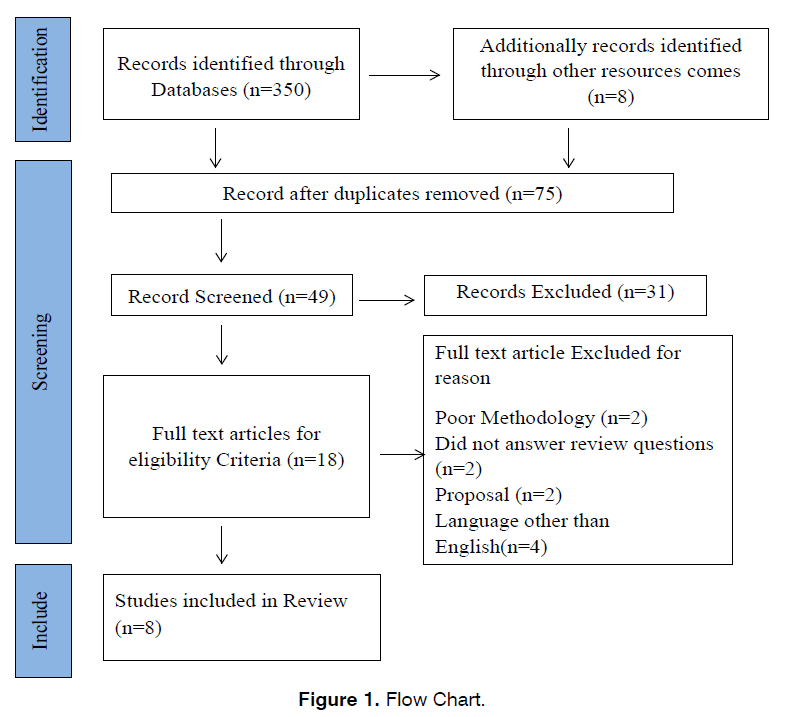
Figure 1: Flow Chart.
Quality Assessment
The quality assessment of the selected studies therefore entailed consideration of their methodological stand and suitability in the Saudi context. Each of the eight articles included in the review was critically evaluated using factors like, clarity of study aim, suitability of the study design and the quality of the findings. All the studies were given scores based on the extent that the study had a higher chance of offering valid and applicable information on the quality of nursing care of patients with tinnitus. This assessment clarified several aspects about the studies that were included: These aspects are that the studies used are of good quality and they provided important information to the existing review (Table 1).
| Sl.No | Author | Appropriate description of the selection of studies | Does the literature covered all relevant studies | Is the method section describe it? | clear description of findings? | Quality rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alluhaymid et al | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 2 | Abou Shaar et al | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 3 | Alzahrani et al | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Fair |
| 4 | Saati | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 5 | Zabeeri et al | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 6 | Aljuaid et al | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 7 | Alanazi et al | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | fair |
| 8 | Eladl et al | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
Table 1: Quality Assessment of the Research Matrix.
The analysis carried out while assessing the quality of the studies that make up the research matrix shows that the reviewed literature has adopted different levels of rigor. Alluhaymid et al. and Abou Shaar et al., Saati, Zabeeri et al., Aljuaid et al., and Eladl et al. had a clear and comprehensive description of study selection, inclusive of all relevant works as well as coherent methods and findings sections that deserved the ‘Good’ quality rating. However, Alzahrani et al. and Alanazi et al. exhibited some limitations: As for the Alzahrani et al., they did not include all the necessary studies while Alanazi et al. provided poor description of the process of study selection, which is why both works received ‘Fair’ rating. The aspects covered by this assessment show the necessity of profound and explicit disclosure of research outcomes.
Data Synthesis:
Importance in this process was the integration of the eight studies chosen in this review in order to provide an overview of the quality of the nursing care in tinnitus management within Saudi Arabia. The synthesis described some of the areas these papers covered including, efficiency of different nursing activities, patients’ satisfaction and influence on the alleviation of symptoms. The synthesis allowed the presentation of the practices existing at present and revealed the possible gaps in nursing care for tinnitus patients in the Saudi environment at the end of the synthesis based on the results of the studies (Table 2 & 3).
| Author, Year | Objective | Study Design | Sample, Sample Size | Analysis | Results | Recommendation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alluhaymid, Y. M. et al., 2022 | Estimate prevalence rates of headache forms among tinnitus patients, explore tinnitus-headache relationship, and assess effect of headache medications on tinnitus. | Quantitative observational cross-sectional study | 226 patients from Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | Self-administrated electronic questionnaire analysis | Significant association between tinnitus and headaches. Patients taking medications reported less tinnitus. Right/left-sided tinnitus associated with same-sided headaches. | Increase awareness among physicians and patients about the tinnitus-headache relationship. Further studies needed on pathophysiology. | Relationship exists between headaches and tinnitus; medications may have a protective effect. Pathophysiology needs more research. |
| Abou Shaar, B. et al., 2024 | Review imaging and management approaches for tinnitus, emphasizing diagnostic imaging and common presentations. | Clinical review | Not specified | Review of literature and clinical practices | No pulsatile tinnitus commonly associated with hearing loss. Pulsatile tinnitus often linked to vascular issues. | Conduct thorough clinical assessments before imaging; imaging often necessary for pulsatile tinnitus. | Tinnitus often has unknown causes; it can significantly affect quality of life. Comprehensive assessments and imaging are crucial. |
| Alzahrani, L. et al., 2022 | Catalogue experience and management of tinnitus in adults with severe-to-profound hearing loss. | Scoping review | 35 records | Review of literature from various databases | Limited research on tinnitus in severe-to-profound hearing loss. Focus largely on cochlear implants. | More empirical studies needed to understand tinnitus in those with minimal sound access. | Limited research; need for more studies focusing on tinnitus in individuals with severe hearing loss. |
| Saati, H. S., 2024 | Evaluate experiences and support needs of family caregivers and nurses for Alzheimer's patients in Saudi Arabia. | Cross-sectional qualitative study with grounded theory approach | Not specified | Thematic analysis of interviews and qualitative data | Identified six emerging themes including physical, spiritual, and financial factors affecting care. | Develop comprehensive management systems to support caregivers and nurses in Saudi Arabia. | Diverse challenges in caregiving highlight the need for improved support systems. |
| Zabeeri, N. et al., 2020 | Assess knowledge and perception of hearing loss and management modalities in Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia. | Repeated measures study | 330 participants | Analysis of questionnaire responses before and after intervention | Significant increase in knowledge about hearing loss and management post-intervention. | Implement more educational campaigns to further improve public awareness. | Educational campaigns significantly improve public knowledge on hearing loss and management. |
| Aljuaid, S. M. et al., 2021 | Evaluate the relationship between caffeine intake and tinnitus incidence. | Systematic review | 142 studies screened, 4 included | Review of study results on caffeine and tinnitus incidence | Mixed results; some studies found inverse relationship; others found no association. Reduction in caffeine may improve tinnitus severity. | Further research needed to clarify caffeine’s impact on tinnitus. | Caffeine's effect on tinnitus is inconclusive; more research required. |
| Alanazi, A. M. et al., 2023 | Examine health rehabilitation services and their impact on quality of life in Saudi Arabia, highlighting current status and future needs. | Narrative review | Expert opinions and discussion | Narrative discussion of health rehabilitation services | Need for optimized rehabilitation services, including home-based and telehealth options. | Implement holistic and tailored rehabilitation services to improve quality of life. | Urgent need for improved health rehabilitation services in Saudi Arabia. |
| Eladl, H. M. et al., 2022 | Evaluate effectiveness of adding physical therapy to photobiomodulation therapy in treating cervicogenic somatosensory tinnitus. | Randomized controlled trial | 40 patients with CST | Mixed MANOVA analysis of tinnitus and cervical ROM measurements | Significant reduction in tinnitus severity and improvement in cervical ROM with additional physical therapy. | Combine supervised physical therapy with PBMT for enhanced treatment of CST. | Combining physical therapy with PBMT shows positive effects on tinnitus and cervical range of motion. |
Table 2: Research Matrix.
| Theme | Sub-Theme | Trends | Explanation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence and Association | Headache and Tinnitus | Statistically significant association between headaches and tinnitus. | Patients with tinnitus frequently experience headaches, and those with unilateral tinnitus often have unilateral headaches. | Increased awareness and early recognition of the association between tinnitus and headaches are advised. |
| Gender and Age | Females report more tinnitus than males; younger individuals more likely to report tinnitus. | Age and gender play a role in the prevalence of tinnitus, with younger age groups and females being more affected. | Targeted interventions and studies focusing on these demographic factors are recommended. | |
| Diagnostic and Imaging Approaches | Imaging for Tinnitus | Imaging more commonly required for pulsatile tinnitus; no pulsatile tinnitus less so. | Pulsatile tinnitus often reveals underlying vascular or structural issues, whereas no pulsatile tinnitus is frequently related to hearing loss or noise exposure. | Use imaging judiciously based on tinnitus type; focus on comprehensive clinical assessments. |
| Diagnostic Challenges | Underlying causes of tinnitus often remain unknown. | Tinnitus can significantly affect quality of life, but its etiology is frequently unclear, complicating diagnosis and treatment. | Continued research to elucidate the pathophysiology of tinnitus is necessary. | |
| Impact of Treatments | Medication and Tinnitus | Pain medications show a protective effect against tinnitus. | Patients using medications for headache relief are less likely to report tinnitus, suggesting a potential protective effect of these medications. | Further studies to explore the mechanisms behind the protective effects of pain medications on tinnitus. |
| Physical Therapy and Photo biomodulation Therapy | Combined therapy shows significant benefits. | Adding supervised physical therapy to photo biomodulation therapy improves tinnitus symptoms and cervical range of motion more effectively than photo biomodulation alone. | Incorporate supervised physical therapy into treatment plans for tinnitus with cervical involvement. | |
| Awareness and Education | Public Knowledge and Perception | Educational campaigns improve public awareness of hearing loss and tinnitus. | Campaigns effectively increase knowledge about hearing loss and tinnitus management, highlighting the need for ongoing public education. | Implement regular educational campaigns to raise awareness about tinnitus and hearing loss. |
| Rehabilitation Services and Quality of Life | Need for optimization of rehabilitation services for chronic diseases. | The current health rehabilitation services in Saudi Arabia are suboptimal, affecting the quality of life for individuals with chronic diseases. | Improve and tailor rehabilitation services; adopt home-based and telehealth options for better outcomes. | |
| Specific Populations | Tinnitus in Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss | Limited research on tinnitus in individuals with severe-to-profound hearing loss. | There is a lack of focused research on tinnitus among those with severe-to-profound hearing loss, with most studies concentrating on cochlear implants. | Conduct more empirical studies to understand tinnitus in individuals with little or no residual hearing. |
| Family and Caregiver Experiences | Diverse challenges in caregiving for Alzheimer’s patients with tinnitus. | Caregivers face multiple challenges including physical, cultural, and financial burdens, impacting their ability to support Alzheimer’s patients effectively. | Develop comprehensive support systems for caregivers, including training and resources. |
Table 3: Finding indicates themes, sub-themes, Trends, Explanation and potential recommendation.
Discussion
There has been improvement in the understanding of correlation between tinnitus and different health problems, including headaches. Tinnitus and headache are related as Alluhaymid et al. (2022) have also noted all the patients with tinnitus have more frequent and severe headache than non-tinnitus patients. Further evidence supporting this association was provided by evidence to suggest that right sided tinnitus is usually accompanied by right sided headaches and vice versa. This underlines the need to evaluate patients with tinnitus, as it may be an alert for the presence of headache disorders that must be treated as well.
Studies that seek to diagnose tinnitus show that imaging tests are most frequently employed in pulsatile tinnitus, where there may be structural abnormalities in the vessels or growths, for instance, and tumors. Abou Shaar et al. , (2024) points out that non-pulsatile tinnitus, which tends to be often linked with presbycusis or ototoxic medication usually does not require imaging in append ageless form except if experiencing other significant manifestations for instance vertigo or hearing loss. This is why the key to tinnitus and its comorbidities depends on a selective diagnostic approach, where the diagnostician tries to avoid invasive diagnostic procedures whose yields are unlikely to be diagnostic while using procedures that are more likely to be diagnostic.
Multimodal approaches to treating tinnitus have also been tested with some success with research done in recent past on tinnitus treatment yielding mixed results. Supervised physical therapy combined with photo bio-modulation therapy improvement of tinnitus and cervical range of motion was identified by Eladl et al., 2022. This approach differs with the use of pain relieving medications that, according to Alluhaymid et al. (2022) has a protective effect against tinnitus hence, indicating that a combination therapy produces the best results for tinnitus management especially in patients with coexisting headaches.
Concerning the organization of care, patient knowledge and awareness on tinnitus and its management influences the patients’ outcomes. According to Zabeeri et al. (2020), education increases the general knowledge of both hearing loss and tinnitus and increases control and management of both conditions. In addition, Alzahrani et al. (2022) mention that there is a higher need to examine tinnitus in individuals with profound hearing loss as most of the literature available focuses on cochlear implants rather than the tinnitus experience of those with severe-to-profound hearing loss. To build the field forward, it is necessary to use the identified gaps with purposeful research and all-encompassing education programs that engage patients and health care professionals in principles of tinnitus management.
Conclusion
That is why this systematic review highlights a number of deficiencies in the quality of nursing care for tinnitus treatment in Saudi Arabia thus calling for improved measures and guidelines. These weaknesses can be palliated by particular suggestions for the following research and enhancement of tinnitus care in the system of health care. Through assuring that the practices of the nursing suppliers match with the prior standards, there will be a contribution in the improvement of the patient results; which will be beneficial for the general health care end creation of Saudi Arabia in boosting its patient care and quality of health.
Limitation
Thus, one small limitation of this study is connected with the fact that, having limited data on nursing care for tinnitus management in Saudi Arabia, the data available may not be of similar quality or amplitude. It is also necessary to appreciate the fact that most of the studies may not necessarily highlight all the practices in nursing that may lead to some gap in the review. However, the sources may not give the comprehensive list of the current clinical environments to manage the condition or even enhance the existing ways of managing the condition. The results may also be influenced by the publication bias since only the article with positive results is likely to get published. These limitations make the call for higher standard of, and more complex research on this specific area quite necessary.
Recommendation
Therefore, only future primary research with higher methodological quality is proposed for conducting to get more accurate and comparable data on nursing practices in tinnitus. National guidelines on tinnitus care and provisions of periodical training programs for the nurses will enhance the quality of a care provided to a patient. Furthermore, planning will also involve effective coordination of the inter-professional relationship between this health care organization and researchers so that the new evidence produced is integrated into the best ways of addressing tinnitus thereby turning ideas into better patient lives.
References
- Abou Shaar B, Qureshy K, Almalki Y, Khan N. Ringing in the Ears: Approaches to Imaging and Management of Tinnitus. Innov Surg Interv Med. 2024;4(2024):9-13.
- Al Shanqiti AM, Abugad HA, Salama KF. Assessment of Ambient Noise Exposure among Medical Staff in Dental Clinics Center of Dammam Medical Complex, Saudi Arabia. J Ecophysiol Occup Health. 2020:120-7.
- Al-Abdulwahhab AH, Al-Suhibani S, Al-Sharydah AM, Al-Jubran SA, Al-Thuneyyan MA. Multiple dural arteriovenous fistulas manifesting as progressive otalgia and tinnitus and treated using a single session of endovascular embolization. Clin Interv Aging. 2020:2313-20.
- Alanazi AA, ALHarbi MF, AlMutairi AM, AlRashied MA, Abed R. Awareness of audiology and speech-language pathology services among healthcare professionals in Saudi Arabia. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024;71(1):1043.
- Alanazi AM, Almutairi AM, Aldhahi MI, Alotaibi TF, AbuNurah HY, Olayan LH, et al. The intersection of health rehabilitation services with quality of life in Saudi Arabia: Current status and future needs. Simul Healthc 2023;11(3):389.
- AlDajani N, AlDhawi LF, Bahkali RI, Lajami F, Katib A, Miftah F, et al. Saudi Arabian Awareness Of Loud Noises, Ear Health, And Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Pharmacophore. 2023;14(S1):1-11.
- Aljazeeri IA, Alomar A, AlTassan F, Alkhayyal J, Alsanosi A. Cochlear implantation in post-lingual adults: a 25-year experience at King Abdullah Ear Specialist Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2021;42(10):1140.
- Aljuaid SM, Mirza AA, Habib LA, AlHarthi LA, Alansari BM, AlQahtani BG, et al. Does caffeine intake increase the incidence of Tinnitus? A systematic review. Int J Otolaryngol. 2021;25(04):e628-32.
- Alluhaymid YM, Alsiwat LJ, Basodan S, Almomani MO. Relationship between tinnitus and headache in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022;11(9):5500-5.
- Alsaab FA, Alaraifi AK, Alhomaydan WA, Ahmed AZ, Elzubair AG. Hearing impairment in military personnel in Eastern Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med. 2021;28(2):110-6.
- Alzahrani L, Sereda M, Chamouton CS, Haider H, Dewey RS, Hoare DJ. Experience of tinnitus in adults who have severe-to-profound hearing loss: A scoping review. Front Neurol. 2022;13:1004059.
- Eladl HM, Elkholi SM, Eid MM, Abdelbasset WK, Ali ZA, El-Deen HA. Effect of adding a supervised physical therapy exercise program to photobiomodulation therapy in the treatment of cervicogenic somatosensory tinnitus: A randomized controlled study. J Med. 2022;101(31):e29946.
- Kanawi HM, Amoodi HA. Intratympanic Steroid Use for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Current Otolaryngology Practice in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023;25(3):115-23.
- Saati HS. Identifying the Family Experiences of Saudi's Alzheimer's Patients and Exploring the Nursing Perspectives Regarding the Experiences: A Qualitative Study. Int Tinnitus J. 2024;28(1).
- Zabeeri N, Alnaimi SN, Alnoaimi DA, Bamousa RM, Alassaf MA, Alotaibi RO, et al. Knowledge and Perception on Hearing Loss, Hearing Management Modalities, Speech and Language Pathology among General Public in Al-Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.2020.
1Department of ADA’A PIU Supervisor, Ministry of Health, Taif, Saudi Arabia
2Department of Female Medical Ward, Hera General Hospital in Makkah, Taif, Saudi Arabia
3Department of Endoscopy, Armed Forces Hospital in Al-Hada, Taif, Saudi Arabia
4Department of Labor and Delivery, Armed Forces Hospital in Al-Hada, Taif, Saudi Arabia
5Department of Surgical Operations Room, Armed Forces Hospital in Al-Hada, Taif, Saudi Arabia
6Department of Outpatient Clinics, Armed Forces Center for Health Rehabilitation, Taif, Saudi Arabia
7Department of Quality Control, Ministry of Health Branch in Alqassim, Taif, Saudi Arabia
8Department of Surgical Operations Room, Buridah Central Hospital in Alqassim, Taif, Saudi Arabia
9Department of Emergency department, Buridah Central Hospital in Alqassim, Taif, Saudi Arabia
Send correspondence to:
Samia Musaad Almutairi
Department of ADA’A PIU Supervisor, Ministry of Health, Taif, Saudi Arabia, E-mail: dr.samia.almutairi@gmail.com
Paper submitted on September 02, 2024; and Accepted on September 10, 2024
Citation: Samia Musaad Almutairi. Assessing the Quality of Nursing Care in Tinnitus Management: A Systematic Review. Int Tinnitus J. 2024;28(1):198-204


