The International Tinnitus Journal
Official Journal of the Neurootological and Equilibriometric Society
Official Journal of the Brazil Federal District Otorhinolaryngologist Society
ISSN: 0946-5448

Google scholar citation report
Citations : 12717
The International Tinnitus Journal received 12717 citations as per google scholar report
The International Tinnitus Journal peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Excerpta Medica
- Scimago
- SCOPUS
- Publons
- EMBASE
- Google Scholar
- Euro Pub
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Medicus
- Medline
- PubMed
- UGC
- EBSCO
Volume 27, Issue 2 / December 2023
Research Article Pages:231-237
10.5935/0946-5448.20230035
Labyrinthine and Neuroscientific Impact of Schizophrenia in the Criminal Justice System
Authors: Prashant Kumar*, Rana Navneet Roy, Shivakant Prajapati
PDF
Abstract
Schizophrenia, a complex mental illness defined by the World Health Organization, leads to significant life impacts, including psychosis, impaired social interactions, and infringements on human rights. Characterized by a disconnection from reality, as noted by the National Institute of Mental Health, it disrupts cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functioning. The Cleveland Clinic highlights its severe effects on both physical and mental well-being, while the WHO underscores the associated distress and impairment in various life aspects. Stat Pearls emphasizes its symptoms, categorized into positive and negative. This condition intersects significantly with the criminal justice system, often resulting in stigma and further complications. A study from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness identifies predictors of criminal justice system involvement, underscoring the need for addressing co-morbid drug abuse to mitigate these risks. This intersection raises crucial considerations regarding treatment versus punishment, ethical and medico-legal dilemmas, global perspectives, and the need for future policy recommendations and research directions to better manage schizophrenia within the criminal justice system.
Keywords: Schizophrenia, Mental health, World Health Organization (WHO), National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), Criminal Justice System (CJS).
Introduction
Schizophrenia, as delineated by the World Health Organization, is a disorder that precipitates psychosis and profoundly influences myriad facets of a person’s existence. This encompasses their personal welfare, familial bonds, societal engagements, educational accomplishments, and vocational efficacy. Moreover, those afflicted with schizophrenia often confront hurdles like stigmatization, prejudice, and violations of their fundamental rights, which are pervasive dilemmas in society.
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) characterizes schizophrenia as a psychiatric disorder that disrupts an individual’s cognitive processes, emotional responses, and behavioral patterns. Individuals grappling with schizophrenia might seem to have severed ties with reality, a state that can be disconcerting for both the sufferers and their acquaintances. This detachment from the tangible world can render their involvement in customary, daily pursuits markedly arduous [1].
The Cleveland Clinic observes that schizophrenia is a psychiatric ailment exerting profound ramifications on both physiological and psychological health. It perturbs cerebral operations, impeding cognitive faculties, recollection, sensory perceptions, and conduct, potentially leading to adversities across diverse realms of quotidian existence. Interpersonal connections and societal engagements are frequently considerably destabilized in individuals grappling with untreated schizophrenia [2].
The World Health Organization (WHO) underscores the considerable anguish and debilitation schizophrenia inflicts in personal, familial, societal, educational, vocational, and other critical spheres of existence. Individuals with schizophrenia are markedly predisposed to premature mortality, frequently owing to physical maladies like cardiovascular or metabolic disorders [3].
Stat Pearls from the NCBI Bookshelf elaborates that schizophrenia, a nomenclature initially introduced by Eugen Bleuler in 1908, is a functional psychotic disorder. It is distinguished by fallacious convictions, sensory misperceptions, and disruptions in cognition, sensation, and conduct. Symptoms are conventionally classified into positive and negative categories, with positive symptoms encompassing sensory deceptions and delusions, and negative symptoms entailing a diminution in emotional expressivity and other fundamental capacities [4].
In essence, schizophrenia is a multifaceted and debilitating affliction that impinges on diverse dimensions of an individual’s existence, encompassing cognitive, emotional, and social faculties. Its precise etiology remains elusive, but it is understood to be a synthesis of genetic, environmental, and neuro-chemical elements. Therapeutic interventions typically comprise pharmacotherapy, psychotherapeutic modalities, and support mechanisms, aimed at symptom mitigation and enhancement of life quality.
The nexus between schizophrenia and the criminal justice system emerges as an increasingly pressing concern, with those afflicted by schizophrenia and other severe mental pathologies facing an elevated risk of entanglement with the Criminal Justice System (CJS). A study leveraging data from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness pinpointed various prognosticators of CJS involvement in individuals with schizophrenia. These include antecedent adolescent behavioral disorders, younger age and male gender, symptoms of Akathisia (a kinetic disorder), and notably substance misuse. The study posits that addressing concurrent substance misuse in persons with schizophrenia could attenuate the risk of detrimental outcomes linked with CJS entanglement, such as stigma, suffering, and other adverse repercussions, and potentially culminate in economic savings for the criminal justice apparatus [5] Figure 1.
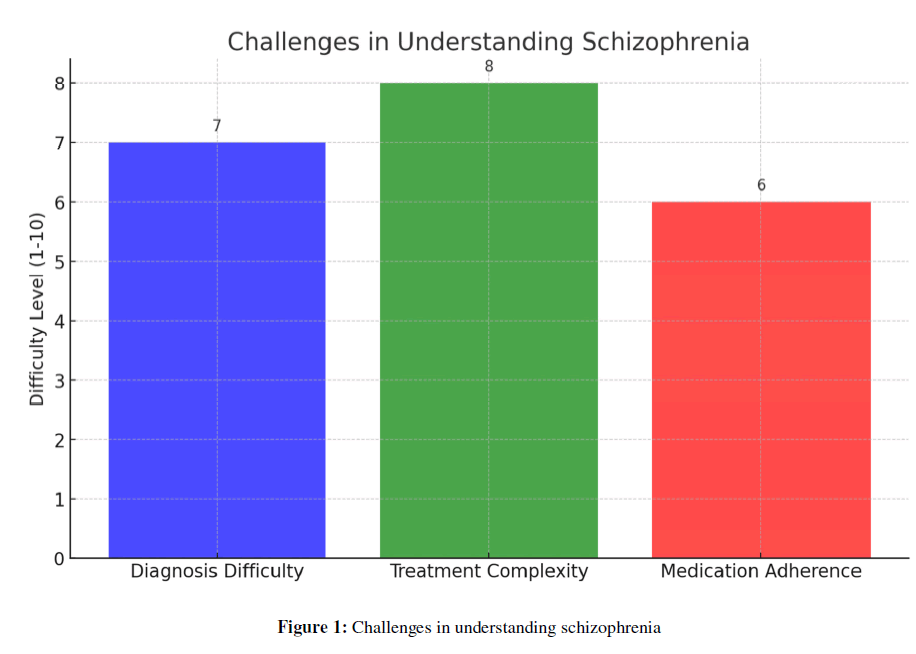
Figure 1: Challenges in understanding schizophrenia.
Challenges in Understanding Schizophrenia
Understanding schizophrenia involves grappling with its complex nature and the challenges it presents in diagnosis and treatment.
Definition and Symptoms: Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder characterized by abnormal interpretation of reality. Key symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking and behavior, and negative symptoms like reduced emotional expression and impaired functioning.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosing schizophrenia is difficult due to its varied and overlapping symptoms with other disorders. Treatment complexity is high, often involving lifelong medication and psychotherapy. A significant challenge is medication adherence, impacted by side effects, patient beliefs, and environmental factors. About 50% of patients struggle with adhering to their medication regimen.
The accompanying graph illustrates these challenges, quantifying the difficulty levels in diagnosis, treatment complexity, and medication adherence, emphasizing the multifaceted approach required in managing schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia in the Criminal Justice System
Prevalence of schizophrenia among incarcerated individuals
The incidence of schizophrenia in the incarcerated populace is markedly elevated relative to the general populace. As per the American Psychological Association, around 10 to 25 percent of U.S. inmates are afflicted with severe mental conditions like major affective disorders or schizophrenia, with as many as 4 percent of prison denizens specifically diagnosed with schizophrenia. This statistic underscores the substantial prevalence of severe mental disorders within the penal population [6].
Cornell University further notes that the rate of mental disorders, including schizophrenia, in the incarcerated population is 3 to 12 times higher than in the general community. This disproportionally high rate of mental disorders among prisoners underscores the need for more focused mental health services within prisons [7].
Additionally, a study cited on Psychiatry Online reports that the prevalence of serious mental illness in jails is nearly four times higher than in the general population. The prevalence of schizophrenia in prisons, in particular, ranges from 2.0% to 6.5%. These statistics indicate a significant challenge for the criminal justice system in providing adequate mental health care and support for incarcerated individuals [8] Figure 2.
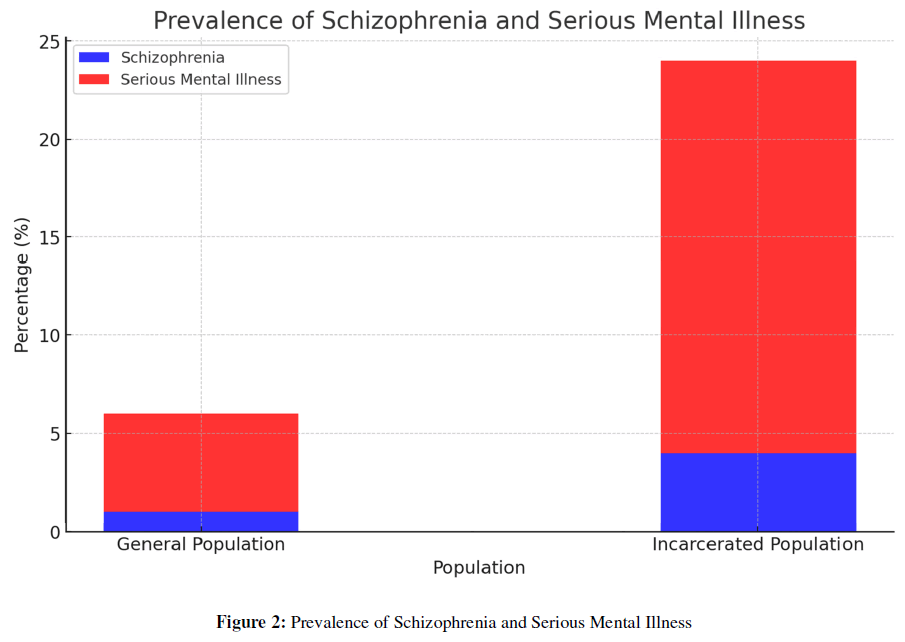
Figure 2: Prevalence of Schizophrenia and Serious Mental Illness.
Note: Here is the analytical graph illustrating the prevalence of schizophrenia and serious mental illnesses in both the general and incarcerated populations. As shown, the percentage of individuals with schizophrenia and other serious mental conditions is significantly higher in the incarcerated population compared to the general population. This visual representation underscores the need for improved mental health services and interventions within the criminal justice system [9].
Case Studies Illustrating the Impact of Schizophrenia in Criminal Behavior
The nexus between schizophrenia and illicit conduct is multifaceted, as demonstrated by a meticulous analysis accessible on PubMed. This scrutiny underscores that schizophrenia is conventionally linked with profound cognitive and emotive impairments, influencing empathetic understanding, discernment abilities, and regulation of impetuousness. The investigation recognizes the correlation between psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia and a diminution in legal culpability, frequently leading to mitigated or nullified criminal responsibility. It accentuates the significance of socio-demographic, developmental, and clinical determinants in this interplay, proposing that the specific deficits inherent in schizophrenia can impact conduct and, thereby, criminal accountability.
Treatment vs. Punishment
The discourse surrounding the choice between imprisonment and rehabilitation for individuals with schizophrenia hinges on the relative efficacy and humanity of punitive versus therapeutic modalities. In the United States, prominent detention facilities like the Los Angeles County Jail, Cook County Jail in Chicago and Riker’s Island Jail in New York harbor a larger population of mentally ill inmates, including those afflicted with schizophrenia, than any psychiatric institution in the nation, as highlighted by Psychology Today. This reflects a prevailing inclination towards confinement rather than medical intervention for those with mental illnesses. According to the Treatment Advocacy Center, approximately one-fifth of inmates in U.S. jails and 15% in state penitentiaries are grappling with serious mental health conditions. The provision of mental health care within these detention centers is often subpar, as these establishments are structured more for penalization than for recovery or psychological treatment. Many inmates, upon thorough assessment, would be more appropriately placed in psychiatric care facilities rather than correctional institutions [10].
Pertaining to the efficacy of therapeutic programs within the penal system, a study available on PubMed reveals that findings of limited robustness prefer non-clozapine antipsychotics over clozapine for the amelioration of psychiatric symptoms in interventions conducted in prisons. Nevertheless, regarding alternative pharmacological treatments, cognitive behavioral therapy, and adapted therapeutic community models, the data is inadequate to formulate conclusive judgments. This underscores the intricacy and inconsistency in the success rates of various treatments in a carceral environment.
For individuals shifting from penal confinement to communal settings, the PubMed analysis revealed that data of limited potency endorsed the efficacy of release planning inclusive of assistance in applying for benefits and combined treatment for dual disorders, as opposed to conventional care, in enhancing the utilization of mental health services and/or diminishing the frequency of psychiatric admissions. However, the available evidence did not suffice to contrast the interventions executed by forensic experts against those implemented by psychiatric practitioners, or to evaluate the relative effectiveness of interpersonal therapy versus psycho-educational approaches for offenders reentering the community [11].
In essence, the discourse contrasting confinement and therapeutic approaches for individuals with schizophrenia encompasses intricate deliberations concerning the efficacy of mental health strategies within the judicial system and a societal propensity towards disciplinary actions. Although there exists partial evidence favoring certain interventions, especially in facilitating the reintegration of these individuals into society, there remains a substantial necessity for further investigation and enhanced execution of efficacious psychiatric treatments within the legal enforcement framework.
Ethical and Medico-Legal Dilemmas
The ethical and medico-legal dilemmas surrounding the sentencing and treatment of individuals with schizophrenia in the criminal justice system revolve around balancing public safety with the rights and needs of mentally ill offenders. There are ongoing debates and varying approaches globally regarding the appropriateness of treatment versus punishment for these individuals.
Ethical Considerations in Sentencing and Treatment: The systematic review on PubMed discusses the complexities in determining criminal responsibility in individuals with schizophrenia. The cognitive and affective deficits associated with schizophrenia, which influence empathy and judgment, often play a role in diminished or abolished criminal liability. However, this relationship is also influenced by socio-demographic, developmental, and clinical factors. These nuances pose ethical dilemmas in sentencing, as the traditional penal system may not be equipped to address the specific needs and rehabilitation of those with serious mental illnesses like schizophrenia [12].
Balancing Public Safety and Rights of Mentally Ill Offenders: According to the Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, there is no clear-cut solution to balancing the rights of mentally ill individuals to receive appropriate treatment and the responsibility of ensuring public safety. In many countries, the legal system allows for both incarceration and hospitalization, sometimes in conjunction, with the sequence varying based on the case. The public often struggles with accepting the release of mentally ill individuals who have committed crimes, especially if the crimes are serious. This is compounded by the challenge of predicting future risks and the potential threat to public safety [13].
Legal Cases and Precedents: The same reference elucidates certain exemplars that underscore the intricacies of this matter. For example, an individual afflicted with schizophrenia, responsible for a grave offense, was adjudicated as mentally disordered yet culpable by a jury, recognizing their cognizance of the act’s essence and repercussions. Such instances highlight the judicial system’s quandary in striking equilibrium between recognizing mental pathology and imposing responsibility on individuals for their deeds, particularly when societal security is jeopardized. These insights reveal the ethical and legal complexities in dealing with schizophrenia within the criminal justice system. The need for a nuanced approach that considers both the treatment needs of the mentally ill and the safety of the public is clear, yet the implementation of such an approach remains challenging and varies significantly across different legal jurisdictions [14].
Comparative Study of Schizophrenia in Criminal Justice System: UK, USA and India
The approaches to schizophrenia in the criminal justice systems of the UK, USA, and India reveal varying practices and challenges Figure 3:
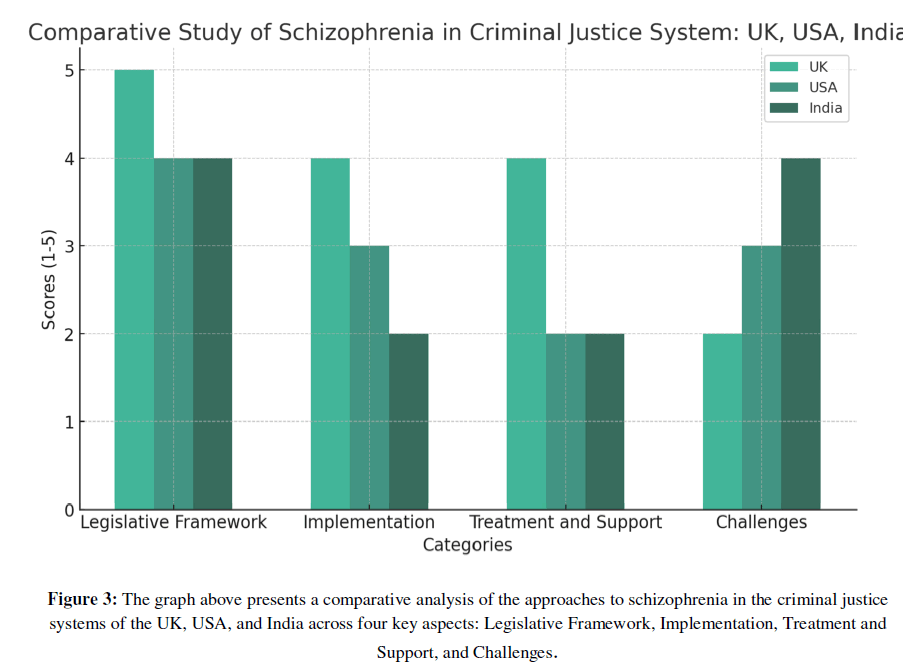
Figure 3: The graph above presents a comparative analysis of the approaches to schizophrenia in the criminal justice systems of the UK, USA, and India across four key aspects: Legislative Framework, Implementation, Treatment and Support, and Challenges.
Note: The graph above presents a comparative analysis of the approaches to schizophrenia in the criminal justice systems of the UK, USA, and India across four key aspects: Legislative Framework, Implementation, Treatment and Support, and Challenges.
United Kingdom
Updated Guidance for Prosecutors: The Crown Prosecution Service (CPS) in the UK has revised its guidance to assist decision-making throughout the criminal case life cycle, from the initial decision to prosecute sentencing. This update reflects a growing understanding of mental health conditions, including schizophrenia.
Consultation and Public Input: A consultation process allows public, charity, and professional feedback before finalizing the guidance, emphasizing community and expert involvement.
Key Information in Guidance: The guidance includes information about different mental health conditions, admissibility of confessions, potential legal defenses, and community treatments or non-criminal justice diversions for defendants with mental illnesses like schizophrenia.
Support for Defendants: The CPS emphasizes reasonable adjustments to support defendants with mental health issues, like using special measures in court to alleviate anxiety [15].
United States
Challenges in Fair Judgment: The US criminal justice system faces challenges in making fair judgments involving schizophrenic individuals due to a lack of reliable prognoses and diagnoses, and clear standards and guidelines.
Insanity Pleas and Sentencing: There’s a tendency to avoid insanity pleas as the indeterminate sentence for insanity can be longer than if found guilty. This often results in schizophrenic offenders receiving little or no psychiatric treatment.
Need for Scientific Approach: The papers suggest the need for a system of scientific diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment to avoid tragedies resulting from inappropriate handling of schizophrenic offenders [16].
India
Mental Healthcare Act of 2017: This act mandates compulsory training for medical officers in prisons and requires each state to establish a Mental Health Establishment in at least one prison.
Gap between Legislation and Implementation: Despite the legislative framework, there is a significant gap in implementation, as evidenced by the lack of resident psychiatrists and inadequate mental health treatment in prisons like Mumbai’s YerawadaJail [17].
Criminal Procedure Code Provisions: The CrPC allows for the release or bail of the accused if found to be mentally unstable during inquiry or trial. However, there are loopholes and challenges in these provisions, impacting fair trials and treatment.
Lack of Comprehensive Mental State Reports: There is no mandate for medical officers to report on the mental state of arrested individuals, impacting their treatment and the understanding of their criminal behavior.
Exclusion in Legal Representation: Individuals grappling with mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, frequently encounter ostracization in legal representation, erecting impediments to equitable access to jurisprudence [18].
In summary, while each country has its legislative framework and guidelines to address schizophrenia in the criminal justice system, the implementation and practical challenges differ significantly. The UK focuses on comprehensive guidance for prosecutors, the USA struggles with fair judgment and treatment standards, and India faces a gap between legislation and its onground implementation.
Future Directions and Policy Recommendations
Current developments in the handling of schizophrenia within the legal framework are characterized by a transition towards consolidated psychiatric care services. This approach involves the criminal justice system collaborating extensively with mental health experts to deliver prompt and efficacious therapy. The employment of technological solutions, notably telepsychiatry, is burgeoning to amplify access to psychiatric care for detainees. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on specialized education for law enforcement and legal practitioners in mental health cognizance.
Regarding policy proposals and prospective scholarly inquiries, there’s a pronounced imperative for the augmentation of psychiatric screening and evaluation mechanisms throughout the judicial system’s various phases. The extension of diversion initiatives is pivotal, as these schemes can reroute individuals with schizophrenia from the judicial system to pertinent mental health services13. Synergistic tactics between the criminal justice and psychiatric sectors are crucial to guarantee seamless and exhaustive care. Legislative reforms focused on diminishing the penalization of mental health issues and advocating therapeutic solutions over penal confinement are also essential. Furthermore, devoting resources to research for pinpointing efficacious strategies and optimal practices in managing schizophrenia within the legal framework is of utmost importance. These suggestions aspire to cultivate a more compassionate and efficient modality, enhancing the welfare of individuals with mental health disorders within the criminal justice environment.
Conclusion
In summarizing the discourse on schizophrenia within the judicial system, it becomes clear that a critical equilibrium between therapeutic intervention and penalization must be upheld. This equipoise is frequently entangled in ethical and medico legal quandaries, where the imperatives of public security, equity, and the individual’s entitlement to adequate mental health care converge. Global comparative scrutiny reveals varied methodologies and hurdles, underscoring the need for contextually nuanced policies, tailored to distinct legal and cultural milieus. Prospective trajectories and policy suggestions emphasize the significance of integrated psychiatric services, enlightened legislative alterations, and ongoing inquiry to evolve and adjust to the unfolding necessities and insights pertaining to schizophrenia in the legal context. The overarching objective should be to forge a more equitable and humane system that proficiently addresses both the legal and psychological dimensions of schizophrenia.
References
- National Institute of Mental Health. Schizophrenia. 2023.
- Cleveland Clinic. Schizophrenia: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment.
- World Health Organization. Schizophrenia - World Health Organization (WHO). 2023.
- Schizophrenia- Stat Pearls. 2023.
- Gross NR, Morgan RD. Understanding persons with mental illness who are and are not criminal justice involved: A comparison of criminal thinking and psychiatric symptoms. Law Hum Behav. 2013;37(3):175.
- Incarceration nation. American Psychological Association. 2014.
- Incarceration and Mental Health. Cornell University. 2023.
- Ford E. First-episode psychosis in the criminal justice system: identifying a critical intercept for early intervention. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2015;23(3):167-75.
- Ascher-Svanum H, Nyhuis AW, Faries DE, Ball DE, Kinon BJ. Involvement in the US criminal justice system and cost implications for persons treated for schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10(1):1-0.
- Melamed Y. Mentally ill persons who commit crimes: punishment or treatment?. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2010;38(1):100-3.
- Fontanarosa J, Uhl S, Oyesanmi O, Schoelles KM. Interventions for adult offenders with serious mental illness.
- Tsimploulis G, Niveau G, Eytan A, Giannakopoulos P, Sentissi O. Schizophrenia and criminal responsibility: A systematic review. J Nerv Ment. 2018;206(5):370-7.
- Greenberg G, Rosenheck RA, Erickson SK, Desai RA, Stefanovics EA, Swartz M, et al. Criminal justice system involvement among people with schizophrenia. Community Ment Health J. 2011;47:727-36.
- Walsh A, Yun I. Schizophrenia: Causes, crime, and implications for criminology and criminal justice. Int J Law Crime Justice. 2013;41(2):188-202.
- New guidance for prosecutors on mental health conditions and disorders. Crown Prosecution Service. 2023.
- Mental Illness and the Justice System. The Crime Report. 2022.
- Challenges for the implementation of the Mental Health Care Act 2017. Br J Psychiatry. 2019.
- TCR Staff. The Central Role India’s Courts Have Played to Protect People with Mental Illness. Wire Science. 2023.
1MATS Law School, MATS University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh (India)
2Hidayatullah National Law University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh (India)
3MATS Law School, MATS University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh (India)
Send correspondence to:
Rana Navneet Roy
Hidayatullah National Law University, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India, Pin- 493661, E-mail: rananavneetroy@gmail.com
Tel: (91) 9303758630
Paper submitted on November 17, 2023; and Accepted December 08, 2023
Citation: Kumar P, Roy NR, Prajapati S. Neuropsychiatric Puzzles: Dissecting the Medico-Legal Complexities of Schizophrenia in the Criminal Justice System. Int Tinnitus J. 2023;27(2):231-237.


